How Long Does Compression Molding Take? | Compression Molding Process & Cycle Time
Join Date: 2024-10-05
Compression molding is a widely used manufacturing process for producing high-strength components from composite materials, thermoplastics, and thermoset plastics. The time it takes to complete one molding cycle—known as the cycle time—varies depending on several key factors. In this article, we will explore what influences compression molding time and how long it typically takes to complete a compression molding process.
Factors That Affect Compression Molding Time
Several factors can affect the length of a compression molding cycle. Below are the most important considerations:
-
Material Type: Thermoset materials like SMC (Sheet Molding Compound) and BMC (Bulk Molding Compound) usually take longer because they require curing. Thermoplastics generally have shorter molding times because they do not need curing.
-
Mold Design: Complex mold designs with intricate shapes take more time to fill and cure. Efficient mold design can minimize cycle time.
-
Part Thickness: Thicker parts require longer time for heat to penetrate evenly, resulting in longer cycle times.
-
Temperature: Higher mold temperatures can reduce curing or melting times, but excessive heat may cause defects.
-
Curing Time: Curing ensures that thermoset materials harden properly. The required curing time can range from minutes to over 30 minutes, depending on the material and part size.


Typical Compression Molding Cycle Time
The cycle time for compression molding typically ranges from 1 to 10 minutes, but it can be longer for complex parts or larger components. The specific time depends on the material, mold design, and part size:
-
Simple Parts: Thin, uncomplicated parts made from thermoplastic materials may have a cycle time of 30 seconds to 2 minutes.
-
Complex Parts: For parts made from thermoset materials like SMC or BMC, the cycle time is usually between 5 to 10 minutes.
-
Thicker Parts: Larger or thicker parts requiring more material and time to cure may extend the cycle time beyond 10 minutes.
For high-volume production environments, such as in automotive or aerospace component manufacturing, optimizing cycle time is crucial for efficiency. Manufacturers constantly aim to reduce cycle time without compromising product quality.
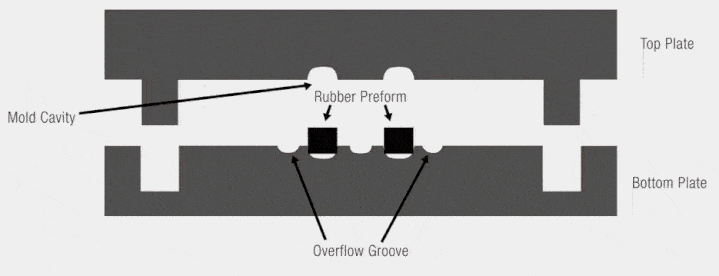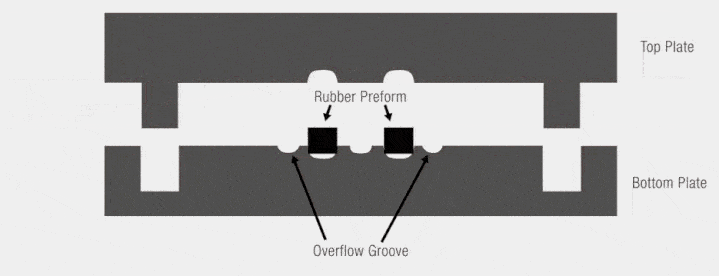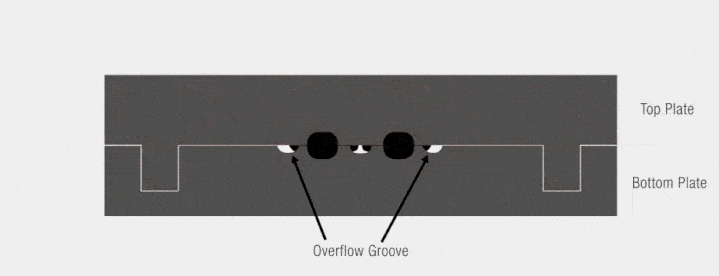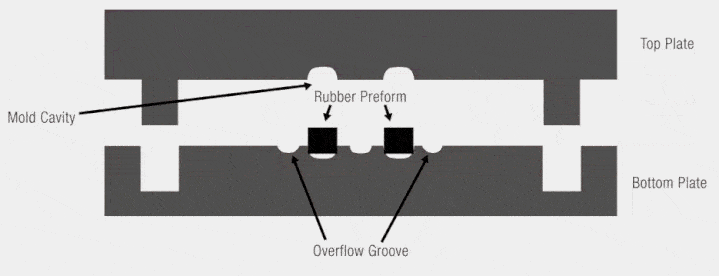
Compression Molding Process Breakdown
Here’s a breakdown of the typical stages of the compression molding process and their respective timeframes:
-
Preheating (Optional): Preheating the material can reduce cycle time and takes around 1 to 3 minutes.
-
Material Loading: The material is placed into the mold, which usually takes 30 seconds to 1 minute.
-
Mold Closing and Pressing: The mold is closed, and heat and pressure are applied, lasting 30 seconds to 10 minutes.
-
Curing Time: This step is crucial for thermoset materials, with times ranging from 2 to 15 minutes.
-
Cooling (Optional): Some thermoplastic parts may require a cooling phase, lasting 1 to 3 minutes.
-
Part Ejection: Once the part is cured or cooled, it is ejected from the mold, taking 10 to 30 seconds.
Strategies for Reducing Compression Molding Time
There are several ways to reduce cycle time in compression molding without sacrificing quality:
-
Optimize Material Flow: Improving material flow can ensure faster filling of the mold cavity.
-
Preheating: Preheating the material before molding reduces pressing and curing times.
-
Automation: Automated loading and ejection systems can streamline the process.
-
Multi-Cavity Molds: Using molds with multiple cavities allows multiple parts to be produced simultaneously.
-
Optimize Mold Temperature: Advanced temperature control systems can maintain optimal mold temperatures to reduce cycle time.

Conclusion
Compression molding time can vary significantly based on factors like material type, part thickness, mold design, and temperature. The cycle time typically ranges from 1 to 10 minutes, but larger or more complex parts may require more time. Manufacturers who optimize key aspects of the process, such as curing time, material flow, and automation, can significantly reduce cycle times and improve production efficiency.
Understanding how long compression molding takes is essential for managing production schedules and meeting delivery timelines, especially in industries like automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods.





